Android Architecture
Android Architecture is a layered framework that outlines the core components and design principles
Android Architecture
Android Architecture provides a structured framework that simplifies the development of efficient, secure, and scalable mobile applications. By organizing the complex system into well-defined layers and components, it helps developers manage app functionality more effectively, ensures better performance, and enhances security. This layered approach also promotes modularity and reusability, making it easier to update and maintain applications over time, ultimately delivering a seamless experience to users.
To Download Our Brochure: https://www.justacademy.co/download-brochure-for-free
Message us for more information: +91 9987184296
Android Architecture provides a structured framework that simplifies the development of efficient, secure, and scalable mobile applications. By organizing the complex system into well defined layers and components, it helps developers manage app functionality more effectively, ensures better performance, and enhances security. This layered approach also promotes modularity and reusability, making it easier to update and maintain applications over time, ultimately delivering a seamless experience to users.
Course Overview
The Android Architecture course provides an overview of the essential components and layers of the Android system, covering topics such as the Linux Kernel, Android Runtime, Application Framework, and more. Through real-time projects and hands-on learning, students will gain a solid understanding of how Android applications are structured, operate, and communicate across different layers, equipping them with the skills to develop efficient, scalable, and secure Android apps.
Course Description
The Android Architecture course offers a concise overview of the key components and layers of Android systems, focusing on how applications interact within the platform. Covering topics like the Linux Kernel, Android Runtime, and Application Framework, it provides practical insights through real-time projects, enabling learners to understand Android app structure and development efficiently.
Key Features
1 - Comprehensive Tool Coverage: Provides hands-on training with a range of industry-standard testing tools, including Selenium, JIRA, LoadRunner, and TestRail.
2) Practical Exercises: Features real-world exercises and case studies to apply tools in various testing scenarios.
3) Interactive Learning: Includes interactive sessions with industry experts for personalized feedback and guidance.
4) Detailed Tutorials: Offers extensive tutorials and documentation on tool functionalities and best practices.
5) Advanced Techniques: Covers both fundamental and advanced techniques for using testing tools effectively.
6) Data Visualization: Integrates tools for visualizing test metrics and results, enhancing data interpretation and decision-making.
7) Tool Integration: Teaches how to integrate testing tools into the software development lifecycle for streamlined workflows.
8) Project-Based Learning: Focuses on project-based learning to build practical skills and create a portfolio of completed tasks.
9) Career Support: Provides resources and support for applying learned skills to real-world job scenarios, including resume building and interview preparation.
10) Up-to-Date Content: Ensures that course materials reflect the latest industry standards and tool updates.
Benefits of taking our course
Functional Tools
1 - Android Studio: The primary Integrated Development Environment (IDE) for Android development, Android Studio offers a comprehensive platform for coding, designing, testing, and debugging Android applications. It includes advanced code editors, UI design tools, and emulator support, enabling students to build and fine tune apps efficiently. The suite of integrated tools helps in managing project files, version control, and performance profiling, making it an all in one solution for Android developers. Learning to navigate Android Studio is fundamental for developing, testing, and deploying professional grade applications. Its user friendly interface and robust features enhance productivity and streamline the development process.
2) Gradle Build System: Gradle functions as the automation tool for building, testing, and packaging Android apps. It manages dependencies, configurations, and build variants seamlessly, allowing students to understand the entire build lifecycle. By mastering Gradle, learners can optimize build times and customize build processes according to project requirements. This tool also helps in managing different build flavors, signing configurations, and integration with continuous deployment pipelines. Gaining expertise in Gradle prepares students for complex project setups and deployment strategies essential in industry environments.
3) Android Debug Bridge (ADB): ADB is a versatile command line tool that facilitates communication between a development machine and Android devices or emulators. It allows students to install and debug applications directly on devices, view logs, and perform device management tasks. ADB is critical for troubleshooting, profiling, and testing applications in real time, ensuring stability and performance. Mastering ADB enables an efficient workflow for app deployment and debugging, making it an indispensable tool in the Android development toolkit.
4) Emulator and Virtual Devices: The Android Emulator provides a simulated environment to test applications across various device configurations, screen sizes, and OS versions. It allows students to emulate different hardware features, network conditions, and sensors, offering a versatile testing ground without requiring physical devices. Learning to use emulators effectively helps students troubleshoot device specific issues and optimize app performance across diverse user scenarios. It also accelerates development cycles by providing instant feedback, testing, and debugging options.
5) Android SDK (Software Development Kit): The SDK contains essential libraries, APIs, and tools required to develop Android applications. It provides framework components, user interface controls, and access to device hardware features. Familiarity with the SDK enables learners to utilize various APIs for sensors, multimedia, data storage, and connectivity. It also facilitates the integration of third party libraries, enhancing app functionality and robustness. Staying updated with the SDK ensures compatibility with the latest Android features and security standards.
6) Android Profiler: Integrated within Android Studio, the profiling tools help monitor app performance, including CPU, memory, network, and energy usage. Students learn to identify bottlenecks, memory leaks, and inefficient code segments that can degrade user experience. The profiler provides real time insights and visualization, empowering learners to optimize their applications for better responsiveness and resource management. Mastering this tool is vital for developing high performance, scalable Android apps.
7) Version Control Systems (e.g., Git): Version control provides a systematic way to manage code revisions, collaborate with teams, and track project changes over time. Students are introduced to Git, which is widely used in industry, enabling them to practice mini projects with proper code management. Learning to use repositories like GitHub or Bitbucket fosters collaboration, code review, and continuous integration practices. This foundational skill is crucial for professional development and maintaining organized codebases.
8) Firebase and Cloud Tools: Firebase offers cloud based services such as real time databases, authentication, hosting, and analytics, simplifying backend integration for Android apps. Students explore how to connect their applications with cloud services, enabling features like real time data sync and user management. Understanding Firebase allows for rapid development of scalable and feature rich apps without extensive backend coding. This tool enhances the capability to build dynamic, real time applications that can handle growing user bases efficiently.
9) Testing Frameworks: Tools like Espresso, UI Automator, and JUnit are essential for implementing automated testing within Android projects. Students learn to write test cases that ensure app stability, functionality, and performance, reducing bugs and improving quality assurance. Automation testing practices accelerate development cycles and facilitate continuous integration processes. Mastery of these frameworks ensures robust app releases and high user satisfaction.
10) API Testing Tools: Postman and other API testing tools are introduced to help students test network requests, backend integrations, and API endpoints used within Android applications. These tools aid in debugging data flow issues, ensuring secure and reliable communication between apps and servers. Familiarity with API testing supports creating resilient applications capable of handling network variances and backend failures effectively.
11 - Material Design Guidelines: Understanding Google’s Material Design principles helps students create visually appealing, intuitive, and consistent user interfaces across Android applications. Learning to implement components such as buttons, cards, navigation drawers, and animations ensures their apps meet modern usability standards. Adhering to Material Design enhances user experience, accessibility, and brand consistency, making applications more professional and engaging.
12) Live Data and ViewModel Architecture Components: These components enable effective data management and UI updates following the MVVM (Model View ViewModel) architecture. Students learn to handle lifecycle aware data, ensuring smooth UI interactions and preventing memory leaks. This knowledge helps in building scalable, maintainable apps with clear separation of concerns, improving code reusability and testing.
13) Kotlin Programming Language: With the adoption of Kotlin as the preferred language for Android development, students are trained in this modern, concise, and expressive language. Learning Kotlin improves code readability, reduces boilerplate, and integrates seamlessly with Android Studio. Mastery of Kotlin prepares learners for a wide range of Android projects and industry standards.
14) Jetpack Compose: This modern toolkit simplifies UI development with declarative programming paradigms. Students explore how to build reactive, flexible, and beautiful interfaces using a more intuitive syntax. Understanding Jetpack Compose accelerates UI creation and makes it easier to implement complex animations and transitions, enhancing app aesthetics and responsiveness.
15) Dependency Injection Frameworks (e.g., Dagger, Hilt): These frameworks promote modular, testable, and maintainable code by managing object dependencies systematically. Students learn to implement dependency injection in their projects, facilitating better code organization and reducing tight coupling. This knowledge is vital for developing scalable applications aligned with industry best practices.
16) Kotlin Coroutines and Asynchronous Programming: Coroutines simplify managing background tasks, such as network calls or database operations, without blocking the main thread. Students learn to write asynchronous code that's easier to read and maintain. Proficiency in coroutines leads to smoother user experiences by keeping apps responsive during intensive operations.
17) Android Security Best Practices: Covering data encryption, secure storage, user authentication, and permission management, students acquire skills to build safe and user trustworthy applications. Understanding security considerations is critical to protect sensitive data and comply with data privacy regulations, ensuring app integrity.
18) Localization and Internationalization: Students explore techniques to adapt apps for multiple languages and regions, including resource management and layout adjustments. This knowledge broadens their ability to develop globally accessible applications, expanding market reach and user inclusivity.
19) App Deployment and Publishing: The course covers preparing applications for release, creating signed APKs, managing app store listings, and understanding update strategies. Students gain practical skills to publish and maintain their apps on Google Play Store, navigating the app submission and review process confidently.
20) Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Implementing CI/CD pipelines automates building, testing, and deploying apps, streamlining the development lifecycle. Students learn to set up tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or Bitrise, reinforcing industry standards for rapid, reliable releases and updates.
21 - Cross Platform Development Frameworks (e.g., Flutter, React Native): Introducing these frameworks enables students to develop applications for multiple platforms using a single codebase. Understanding cross platform tools broadens their skill set, and prepares them to work on versatile projects that reach a wider audience efficiently.
22) Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): For students interested in immersive technologies, modules on ARCore and related SDKs cover integration of AR and VR experiences within Android apps. This prepares learners for innovative project opportunities in gaming, retail, education, and more.
23) Voice and Gesture Recognition Technologies: Incorporating Android’s speech APIs and gesture controls allows students to create more accessible and interactive applications. Such skills enhance user engagement and add cutting edge features to modern apps.
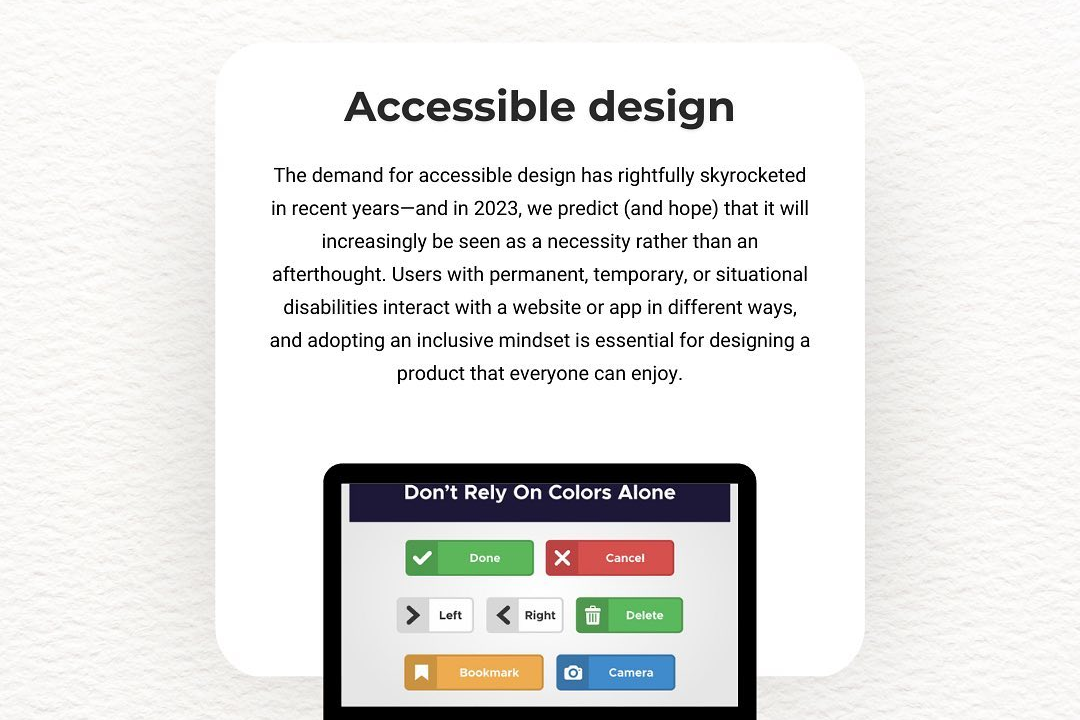
24) Accessibility Features Development: Emphasizing accessibility best practices ensures apps are usable by people with disabilities. Students learn to implement screen readers, adjustable fonts, contrast settings, and other accessibility options, promoting inclusivity.
25) Data Persistence and Local Storage: Courses cover techniques such as SharedPreferences, SQLite databases, and Room persistence library, enabling students to store user data securely on devices. This understanding is crucial for developing apps that function offline and handle user data effectively.
26) User Analytics and Crash Reporting: Integrating tools like Google Analytics and Firebase Crashlytics equips students with insights into user behavior and app stability. Tracking analytics facilitates data driven improvements and supports delivering high quality, user centric applications.
27) In App Billing and Monetization: Students explore implementing in app purchases, subscriptions, and ads to generate revenue from their apps. They learn to manage payment flows securely and in compliance with platform policies, vital for commercial app development.
28) Multiplayer and Real Time Communication: For social, gaming, or collaborative apps, students learn to integrate real time messaging and multiplayer features through Firebase, WebSockets, or third party SDKs, enabling dynamic and interactive experiences.
29) Background Services and Notifications: Understanding how to run background tasks and implement push notifications helps in creating engaging, responsive apps that keep users informed and involved even when not actively using the app.
30) Ethical AI and Data Privacy in App Development: With the rising importance of ethical considerations, students are introduced to responsible AI usage, data privacy laws, and user consent strategies, ensuring their applications adhere to legal standards and ethical norms.
Browse our course links : https://www.justacademy.co/all-courses
To Join our FREE DEMO Session:
This information is sourced from JustAcademy
Contact Info:
Roshan Chaturvedi
Message us on Whatsapp: +91 9987184296
Email id: info@justacademy.co
Sample Files For Use To Learn Power Bi
Comprehensive Guide to Android Architecture: Components, Best Practices, and Design Patterns
Android Architecture Guide: Components, Best Practices, and Design Patterns for Modern App Development
Android App Architecture: Best Practices, Components, and Design Patterns for Efficient Development
Complete Guide to Android App Architecture: Best Practices, Components, and Design Patterns for 2024